分析SpringBoot底层机制¶
Tomcat启动分析,Spring容器初始化,Tomcat如何关联Spring容器?
1.创建SpringBoot环境¶
(1)创建Maven程序,创建SpringBoot环境
(2)pom.xml导入SpringBoot的父工程和依赖
<!--导入SpringBoot父工程-规定写法-->
<parent>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<version>2.5.3</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<!--导入web项目场景启动器:会自动导入和web开发相关的所有依赖[jar包]-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
(3)创建主程序MainApp.java
package com.li.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
@SpringBootApplication//表示SpringBoot项目
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//启动SpringBoot项目
ConfigurableApplicationContext ioc =
SpringApplication.run(MainApp.class, args);
}
}
(4)启动项目,我们可以注意到Tomcat也随之启动了。
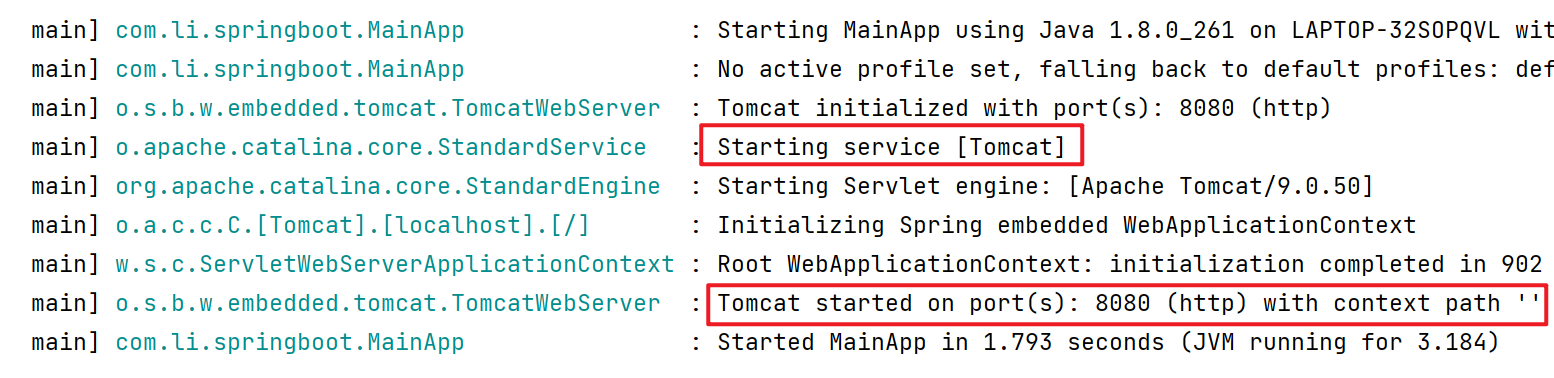
问题一:当我们执行run方法时,为什么会启动我们内置的tomcat?它的底层是如何实现的?
2.Spring容器初始化(@Configuration+@Bean)¶
我们知道,如果在一个类上添加了注解@Configuration,那么这个类就会变成配置类;配置类中通过@Bean注解,可以将方法中 new 出来的Bean对象注入到容器中,该bean对象的id默认为方法名。
配置类本身也会作为bean注入到容器中


容器初始化的底层机制仍然是我们之前分析的Spring容器的机制(IO/文件扫描+注解+反射+集合+映射)
对比:
- Spring通过@ComponentScan,指定要扫描的包;而SpringBoot默认从主程序所在的包开始扫描,同时也可以指定要扫描的包(scanBasePackages = {"xxx.xx"})。
- Spring通过xml或者注解,指定要注入的bean;SpringBoot通过扫描配置类(对应spring的xml)的@Bean或者注解,指定注入bean
3.SpringBoot怎样启动Tomcat,并能支持访问@Controller?¶
由前面的例子1中可以看到,当启动SpringBoot时,tomcat也会随之启动。那么问题来了:
- SpringBoot是怎么内嵌Tomcat,并启动Tomcat的?
- 而且底层是怎样让@Controller修饰的控制器也可以被访问的?
3.1源码分析SpringApplication.run()¶
SpringApplication.run()方法会完成两个重要任务:
- 创建容器
- 容器的刷新:包括参数的刷新+启动Tomcat
(1)创建一个控制器
package com.li.springboot.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* HiController被标注后,作为一个控制器注入容器中
*/
@RestController//相当于@Controller+@ResponseBody
public class HiController {
@RequestMapping("/hi")
public String hi() {
return "hi,HiController";
}
}
(2)启动主程序MainApp.java,进行debug
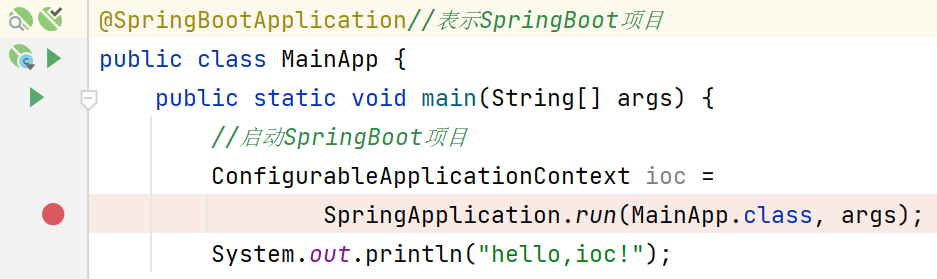
(3)首先进入SpringApplication.java的run方法
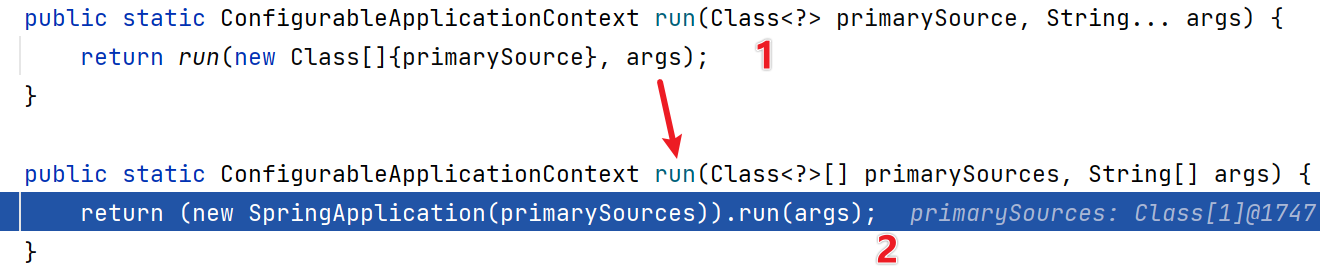
(4)点击step into,进入如下方法
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
...
try {
...
context = this.createApplicationContext();//严重分析,创建容器
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
this.prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
this.refreshContext(context);//刷新应用上下文,比如初始化默认设置/注入相关bean/启动Tomcat
this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
...
} catch (Throwable var10) {...}
...
}
(5)分别对 createApplicationContext() **和 **refreshContext(context) 方法进行分析:
(5.1)step into 进入 **createApplicationContext() ** 方法中:
//springApplication.java
//容器类型很多,会根据你的this.webApplicationType创建对应的容器,默认this.webApplicationType
//的类型为SERVLET,也就是web容器(可以处理servlet)
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
return this.applicationContextFactory.create(this.webApplicationType);
}
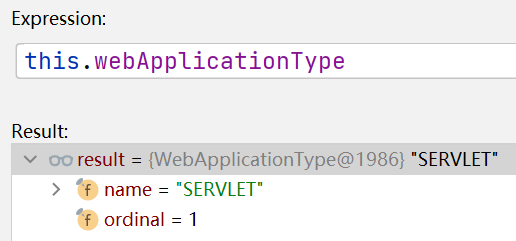
(5.2)点击进入下一层
//接口 ApplicationContextFactory.java
//该方法根据webApplicationType创建不同的容器
ApplicationContextFactory DEFAULT = (webApplicationType) -> {
try {
switch(webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET://默认进入这一分支,返回
//AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext容器
return new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext();
case REACTIVE:
return new AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext();
default:
return new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
}
} catch (Exception var2) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable create a default ApplicationContext instance, you may need a custom ApplicationContextFactory", var2);
}
};
总结:createApplicationContext()方法中创建了容器,但是还没有将bean注入到容器中。
(5.3)step into 进入 refreshContext(context) 方法中:
//springApplication.java
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
shutdownHook.registerApplicationContext(context);
}
this.refresh(context);//核心,真正执行相关任务
}
(5.4)在this.refresh(context);这一步进入下一层:
//springApplication.java
protected void refresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
applicationContext.refresh();
}
(5.5)继续进入下一层:
protected void refresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
applicationContext.refresh();
}
(5.6)继续进入下一层:
//ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
public final void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
try {
super.refresh();
} catch (RuntimeException var3) {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
if (webServer != null) {
webServer.stop();
}
throw var3;
}
}
(5.7)在super.refresh();这一步进入下一层:
//AbstractApplicationContext.java
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
...
try {
...
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
//在上下文的子类初始化指定的bean
onRefresh(); //当父类完成通用的工作后,再重新用动态绑定机制回到子类
...
}
catch (BeansException ex) {...}
finally {...}
}
}
(5.8)在onRefresh();这一步step into,会重新返回上一层:
//ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
this.createWebServer();//创建一个webserver,可以理解成创建我们指定的web服务-Tomcat
} catch (Throwable var2) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", var2);
}
}
(5.9)在this.createWebServer();这一步step into:
//ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
StartupStep createWebServer = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.boot.webserver.create");
ServletWebServerFactory factory = this.getWebServerFactory();
createWebServer.tag("factory", factory.getClass().toString());
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(new ServletContextInitializer[]{this.getSelfInitializer()});//使用TomcatServletWebServerFactory创建一个TomcatWebServer
createWebServer.end();
this.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerGracefulShutdown", new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle(this.webServer));
this.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerStartStop", new WebServerStartStopLifecycle(this, this.webServer));
} else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
this.getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
} catch (ServletException var5) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", var5);
}
}
this.initPropertySources();
}
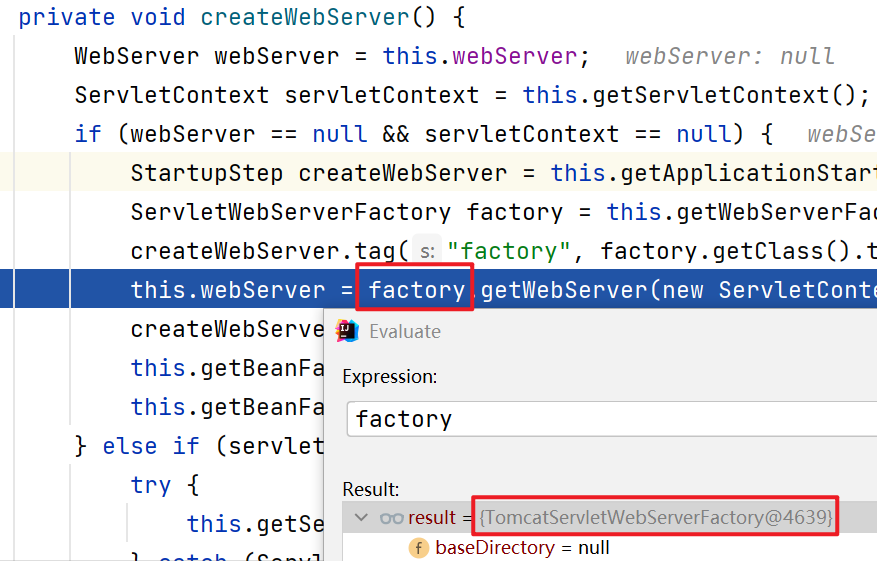
(5.10)在this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(new ServletContextInitializer[]{this.getSelfInitializer()});这一步step into:
//TomcatServletWebServerFactory.java会创建Tomcat,并启动Tomcat
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
Registry.disableRegistry();
}
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();//创建了Tomcat对象,下面是一系列的初始化任务
File baseDir = this.baseDirectory != null ? this.baseDirectory : this.createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
this.customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
this.configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
Iterator var5 = this.additionalTomcatConnectors.iterator();
while(var5.hasNext()) {
Connector additionalConnector = (Connector)var5.next();
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
this.prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return this.getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
(5.11)在return this.getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);这一步step into:
//TomcatServletWebServerFactory.java
//这里做了端口校验,创建了TomcatWebServer
protected TomcatWebServer getTomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat) {
return new TomcatWebServer(tomcat, this.getPort() >= 0, this.getShutdown());
}
(5.12)继续step into进入下一层
//TomcatServletWebServerFactory.java
public TomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat, boolean autoStart, Shutdown shutdown) {
this.monitor = new Object();
this.serviceConnectors = new HashMap();
Assert.notNull(tomcat, "Tomcat Server must not be null");
this.tomcat = tomcat;
this.autoStart = autoStart;
this.gracefulShutdown = shutdown == Shutdown.GRACEFUL ? new GracefulShutdown(tomcat) : null;
this.initialize();//进行初始化,并启动tomcat
}
(5.13)this.initialize();继续step into:
//TomcatServletWebServerFactory.java
private void initialize() throws WebServerException {
logger.info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + this.getPortsDescription(false));
synchronized(this.monitor) {
try {
this.addInstanceIdToEngineName();
Context context = this.findContext();
context.addLifecycleListener((event) -> {
if (context.equals(event.getSource()) && "start".equals(event.getType())) {
this.removeServiceConnectors();
}
});
this.tomcat.start();//启动Tomcat!
this.rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions();
try {
ContextBindings.bindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(), this.getClass().getClassLoader());
} catch (NamingException var5) {
}
this.startDaemonAwaitThread();
} catch (Exception var6) {
this.stopSilently();
this.destroySilently();
throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat", var6);
}
}
}
(6)一路返回上层,然后终于执行完**refreshContext(context)**方法,此时context为已经注入了bean