AOP-02¶
4.问题提出¶
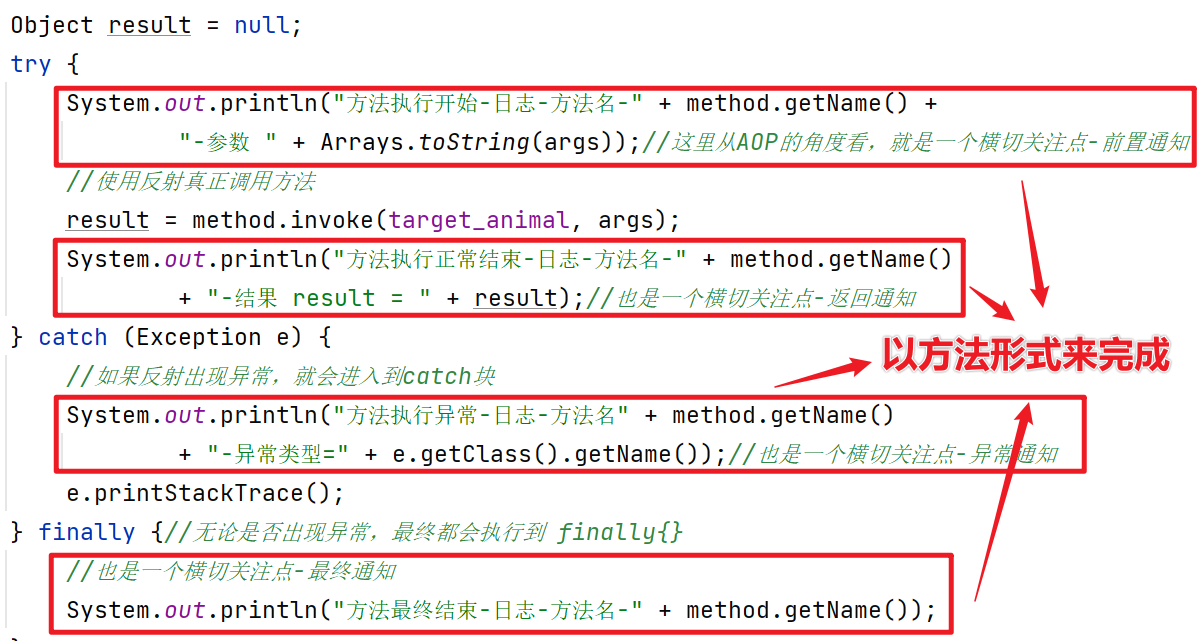
在上一篇的MyProxyProvider类中,我们的输出语句功能比较弱,在实际开发中,我们希望是以一个方法的形式,嵌入到真正执行的目标方法前,怎么办?
1.使用土方法解决
需求分析:使用土方法解决前面的问题,后面使用spring的aop组件完成
改进MyProxyProvider:
主要是对前置/返回/异常/最终通知的代码进行封装,封装到不同的方法中进行调用。
package com.li.aop.proxy3;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 返回一个动态代理对象,可以执行被代理的对象的方法
*/
public class MyProxyProvider {
//定义要执行的目标对象,该对象需要实现 SmartAnimal接口
private SmartAnimal target_animal;
//构造器
public MyProxyProvider(SmartAnimal target_animal) {
this.target_animal = target_animal;
}
//定义一个方法,在目标对象执行前执行
public void before(Method method, Object[] args) {
System.out.println("before-方法执行开始-日志-方法名-" + method.getName() +
"-参数 " + Arrays.toString(args));//AOP的角度看,是一个横切关注点-前置通知
}
//定义一个方法,在目标对象执行后行
public void after(Method method, Object result) {
System.out.println("after-方法执行正常结束-日志-方法名-" + method.getName()
+ "-结果 result = " + result);//也是一个横切关注点-返回通知
}
//定义方法返回代理对象,该代理对象可以执行目标对象
public SmartAnimal getProxy() {
//(1)先得到类加载器对象
ClassLoader classLoader = target_animal.getClass().getClassLoader();
//(2)得到要执行的目标对象的接口信息
Class<?>[] interfaces = target_animal.getClass().getInterfaces();
//(3)使用匿名内部类 创建 InvocationHandler对象
InvocationHandler invocationHandler = new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
try {
before(method, args);
//使用反射真正调用方法
result = method.invoke(target_animal, args);
after(method, result);
} catch (Exception e) {
//如果反射出现异常,就会进入到catch块
System.out.println("方法执行异常-日志-方法名" + method.getName()
+ "-异常类型=" + e.getClass().getName());//横切关注点-异常通知
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {//无论是否出现异常,最终都会执行到 finally{}
//也是一个横切关注点-最终通知
System.out.println("方法最终结束-日志-方法名-" + method.getName());
}
return result;
}
};
//创建代理对象
SmartAnimal proxy = (SmartAnimal) Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, invocationHandler);
return proxy;
}
}
2.对土方法进行解耦-开发简易的AOP类
上面的代码因为前后置等处理方法都写在同一个类中,造成代码耦合度高的问题。因此,更好的解决方法是新建一个类MyAOP,在该类中进行处理方法的编写,然后在MyProxyProvider类中调用该类的方法。
MyAOP类:
package com.li.aop.proxy3;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 自己写的一个极简AOP类
*/
public class MyAOP {
//定义一个方法,在目标对象执行前执行
public static void before(Method method, Object[] args) {
System.out.println("MyAOP-方法执行开始-日志-方法名-" + method.getName() +
"-参数 " + Arrays.toString(args));//前置通知
}
//定义一个方法,在目标对象执行后行
public static void after(Method method, Object result) {
System.out.println("MyAOP-方法执行正常结束-日志-方法名-" + method.getName()
+ "-结果 result = " + result);//返回通知
}
}
3.再次分析-提出Spring AOP
使用上面的办法仍存在一些问题:
- 不够灵活:假设被代理对象有很多方法,而我们只想仅对其中一个方法进行处理,当前的代码还不能实现这个需求
- 复用性差:假如有一个新的接口USBInterface,Phone类实现了这个接口,现在我们想要Phone类去调用之前MyAOP中的方法。但MyAOP类的方法是根据之前的SmartAnimal接口的方法写的,因此不能很好的适用于新的接口及其实现类
- 硬编码:没有注解和反射的支撑
5.AOP的基本介绍¶
1.什么是AOP?
官方文档:核心技术 (spring.io)
AOP全称:aspect oriented programming,即面向切面编程。
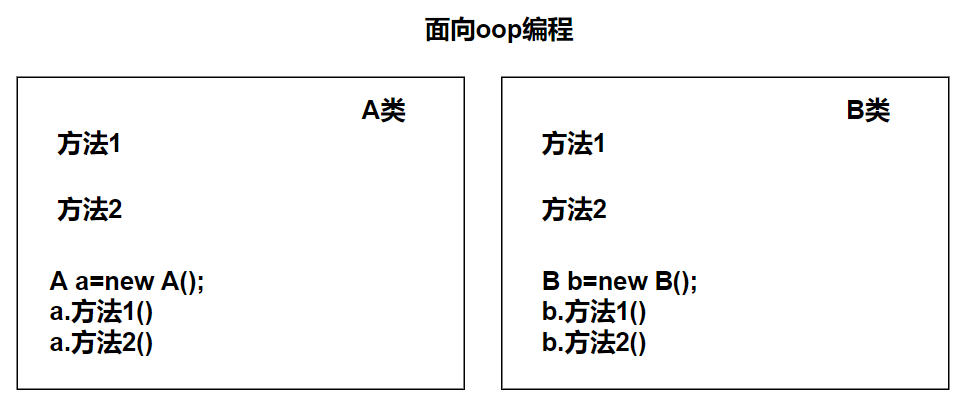
AOP 是一种编程思想,是面向对象编程(OOP)的一种补充。面向对象编程将程序抽象成各个层次的对象,而面向切面编程是将程序抽象成各个切面。
2.AOP和OOP的区别:
OOP 针对业务处理过程的实体及其属性和行为进行抽象封装,以获得更加清晰高效的逻辑单元划分。
而 AOP 则是针对业务处理过程中的切面进行提取,它所面对的是处理过程中的某个步骤或阶段,以获得逻辑过程中各部分之间低耦合性的隔离效果。
这两种设计思想在目标上有着本质的差异:
面向目标不同:简单来说 OOP 是面向名词领域,AOP 面向动词领域。
思想结构不同:OOP 是纵向结构,AOP 是横向结构。
注重方面不同:OOP 注重业务逻辑单元的划分,AOP 偏重业务处理过程中的某个步骤或阶段。
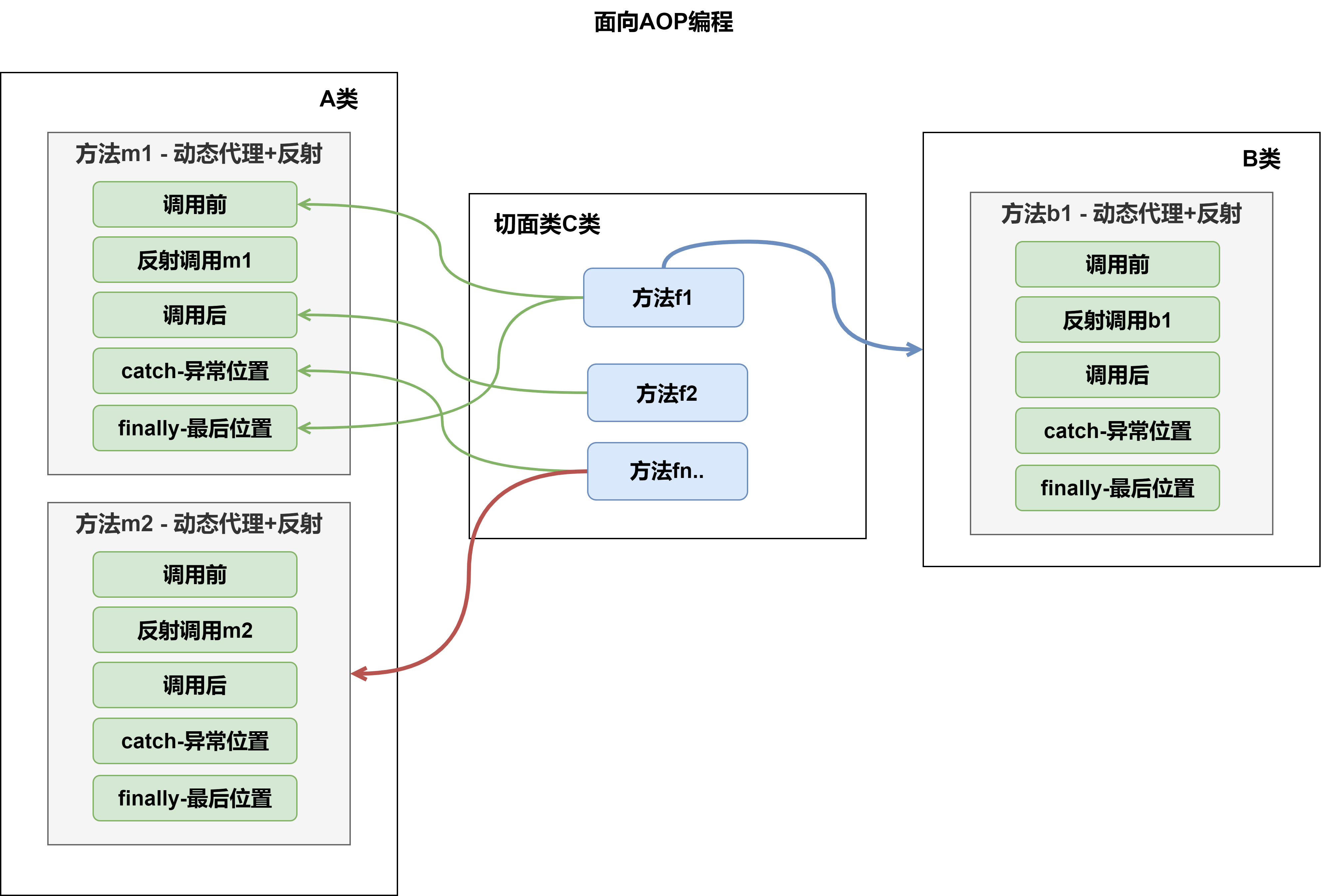
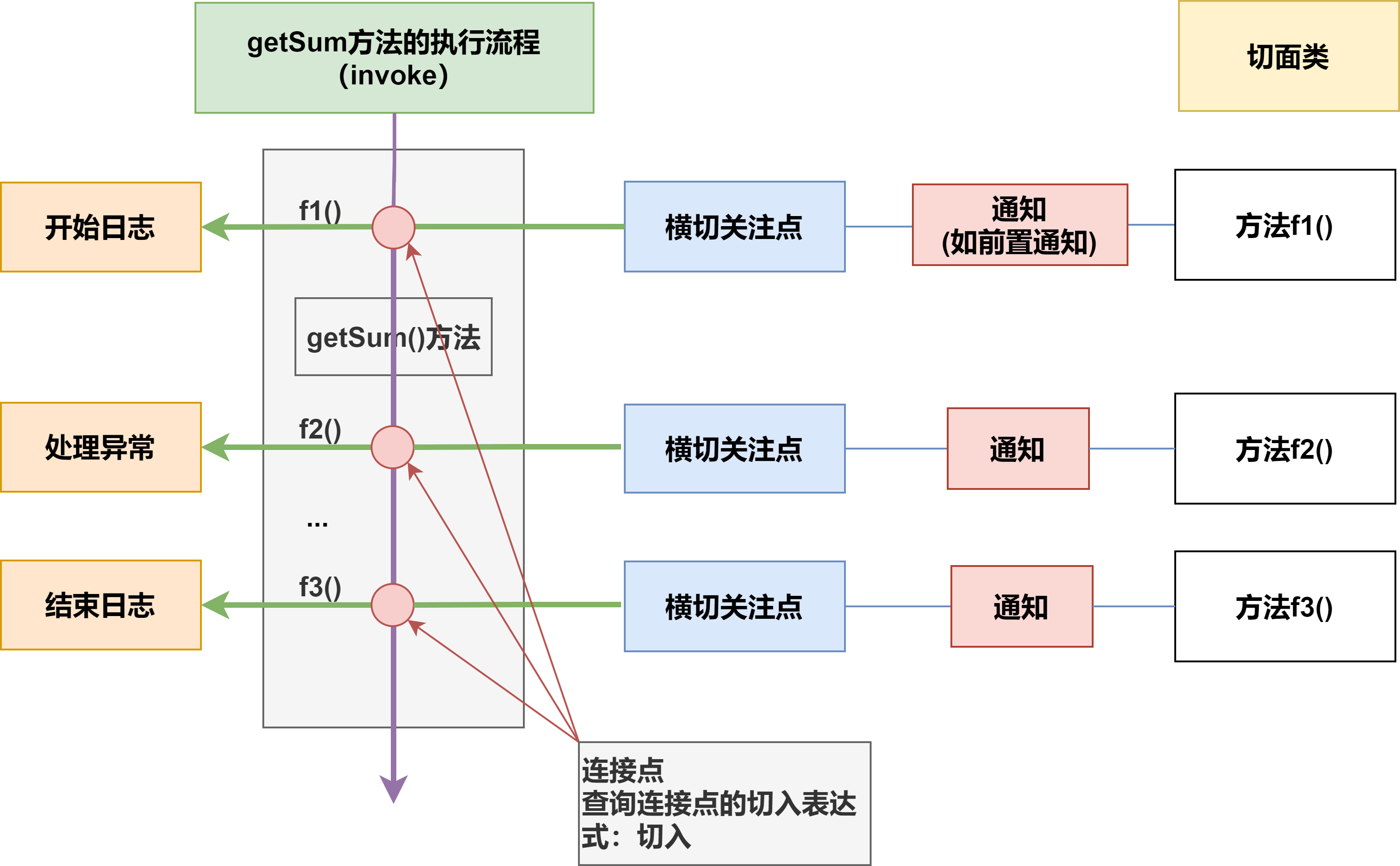
aop通过动态代理+反射的方式,对被代理对象的方法进行调用。
这个被代理对象的方法的调用过程,会拆分成几个横切关注点:
- 方法调用前
- 方法调用
- 方法调用后
- 异常位置(catch块)
- 方法最终调用位置(finally块)
如下,切面类C的不同方法f1……fn可以在不同类A,B......的方法m1,m2......执行的过程中,在方法的不同横切关注点任意切入/调用。
即切面类的任意方法可以在任意类的任意方法执行的过程中,在该方法的不同横切关注点任意切入。
3.AOP的实现方式
- 基于动态代理的方式[内置AOP实现]
- 使用框架aspectj来实现
6.AOP编程快速入门¶
6.1基本说明¶
这里使用框架aspectj来实现:
- 引入核心的aspect包
- 在切面类中声明通知方法
- 前置通知:@Before
- 返回通知:@AfterReturning
- 异常通知:@AfterThrowing
- 后置通知:@After
-
环绕通知:@Around
-
五种通知和前面写的动态代理类方法的对应关系:

6.2快速入门实例¶
使用aop编程的方式,来实现手写的动态代理案例的效果。以上一篇的3.1为例子:
需求说明:有一个SmartAnimal接口,可以完成简单的加减法,要求在执行getSum()和getSub()时,输出执行前、执行过程、执行后的日志输出,请思考如何实现
1.导入AOP编程需要的包

2.代码实现
2.1SmartAnimal接口:
package com.li.aop.aspectj;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
public interface SmartAnimal {
//求和
float getSum(float a, float b);
//求差
float getSub(float a, float b);
}
2.2SmartDog实现类:
package com.li.aop.aspectj;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
//使用component注解,当spring容器启动时,将SmartDog注入容器
@Component
public class SmartDog implements SmartAnimal {
@Override
public float getSum(float a, float b) {
float result = a + b;
System.out.println("方法内部打印 result = " + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public float getSub(float a, float b) {
float result = a - b;
System.out.println("方法内部打印 result = " + result);
return result;
}
}
2.3SmartAnimalAspect切面类:
package com.li.aop.aspectj;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 切面类,类似之前写的 MyProxyProvider,但是功能比它强大得多
*/
@Aspect //表示一个切面类[底层自动注入切面编程的支撑(动态代理+反射+动态绑定)]
@Component //注入切面类到ioc容器
public class SmartAnimalAspect {
/**
* 前置通知
* 1.@Before表示前置通知,即在我们的目标对象执行方法前执行
* 2.value = "execution(public float com.li.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))"
* 指定切入到哪个类的哪个方法 形式为:execution(访问修饰符 返回类型 全类名.方法名(形参列表))
* 3.f1方法就是一个切入方法,方法名随意
* 4.JoinPoint joinPoint 在底层执行时,由AspectJ切面框架,给切入方法传入joinPoint连接点对象
* 通过切面方法,可以获取你想要的信息
*
* @param joinPoint
*/
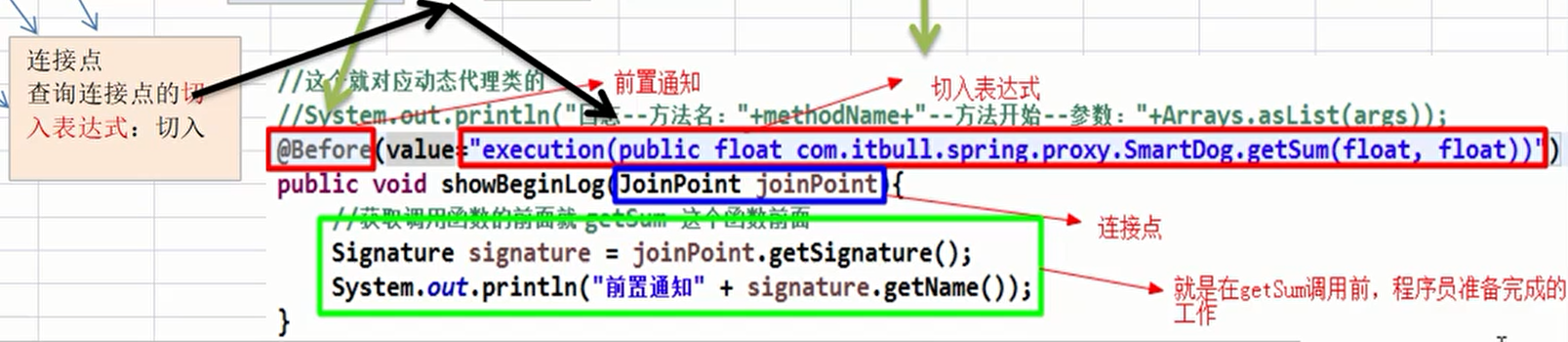
@Before(value = "execution(public float com.li.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))")
public void f1(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
//通过连接点对象joinPoint 拿到方法签名
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类f1()-方法执行开始-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() +
"-参数 " + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
//返回通知:把 f2方法切入到目标对象方法正常执行完毕后的位置
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(public float com.li.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))")
public void f2(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类f2()-方法执行正常结束-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName());
}
//异常通知:把 f3方法切入到目标对象方法出现异常后的catch块位置
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(public float com.li.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))")
public void f3(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类f3()-方法执行异常-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName());
}
//最终通知:把 f4方法切入到目标对象方法执行后的位置,无论有无出现异常都会执行
@After(value = "execution(public float com.li.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))")
public void f4(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类f4()-方法最终执行完毕-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName());
}
}
2.4配置容器文件beans07.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--配置自动扫描的包-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.li.aop.aspectj"/>
<!--一定要开启基于注解的 AOP 功能-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
</beans>
2.5测试类:
package com.li.aop.aspectj;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 测试类
*/
public class AopAspectjTest {
@Test
public void smartDogTestByAspectj() {
//得到Spring容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans07.xml");
//通过接口类型来获得注入的SmartDog对象(实际上是代理对象proxy)
SmartAnimal smartAnimal = ioc.getBean(SmartAnimal.class);
//class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy15
//System.out.println("smartAnimal的运行类型=" + smartAnimal.getClass());
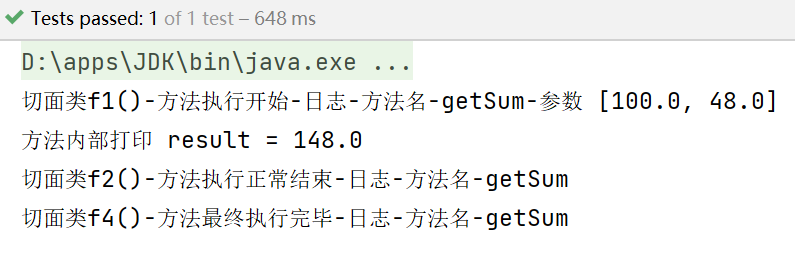
smartAnimal.getSum(100, 48);
}
}
测试结果:
6.3细节说明¶
-
关于切面类方法命名可以自己规范一下
-
切入表达式的更多配置,比如使用模糊配置
形式为:execution(访问修饰符 返回类型 全类名.方法名(形参列表))
@Before(value = "execution(* com.li.aop.aspect.SmartDog.*(..))")
- 下面表示所有访问权限,所有包下所有类的所有方法(前提是基于动态代理的类),都会被执行前置通知方法
@Before(value = "execution(* *.*(..))")
-
spring容器开启了基于注解的AOP功能
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>,获取注入的对象则需要以接口的类型来获取,因为你注入的对象.getClass()已经是代理类型了! -
spring容器开启了基于注解的AOP功能,也可以通过id来获取注入的对象,但也要转成接口类型来获取。
6.4练习¶
- 有一个接口USBInterface,该接口有一个方法work
- 写出实现子类Phone和Camera
- 写一个切面类,在该切面类中写一个方法(可输出日志信息)等作为前置通知,在Phone和Camera对象执行work方法前调用
- 其他通知,如返回通知,异常通知,后置通知,也可以加入
(1)UsbInterface接口:
package com.li.aop.hw;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
public interface UsbInterface {
public void work(String s);
}
(2)Phone实现类:
package com.li.aop.hw;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
@Component //将Phone对象当做组件注入到容器中
public class Phone implements UsbInterface {
@Override
public void work(String s) {
System.out.println("手机开始工作,参数是=" + s);
}
}
(3)Camera实现类:
package com.li.aop.hw;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
@Component
public class Camera implements UsbInterface {
@Override
public void work(String s) {
System.out.println("相机开始工作,参数是=" + s);
}
}
(4)配置容器文件:
<!--配置自动扫描的包-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.li.aop.hw"/>
<!--开启基于注解的aop功能-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
(5)MyAspect切面类:
package com.li.aop.hw;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 切面类
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
//前置通知
@Before(value = "execution(public void com.li.aop.hw.*.work(String))")
public void beforeRunning(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("MyAspect前置通知-目标方法-" + methodName +
" 参数-" + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
//其他通知逻辑相同,略
}
(6)测试类:
package com.li.aop.hw;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
public class UsbTest {
@Test
public void UsbAspectTest() {
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans08.xml");
//获取的实际都是代理对象
UsbInterface phoneProxy = ioc.getBean("phone", UsbInterface.class);
UsbInterface cameraProxy = ioc.getBean("camera", UsbInterface.class);
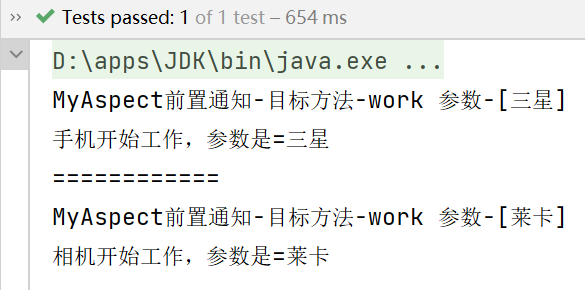
phoneProxy.work("三星");
System.out.println("============");
cameraProxy.work("莱卡");
}
}
测试结果:
需要注意的是,如果测试类中使用接口类型获取bean,是因为当前ioc容器中只有一个代理对象。即只有一个类实现了SmartAnimal接口,因此这里只会有一个代理类。
如果有多个类实现接口,就不能使用接口类型获取bean。单例对象id默认分配的id是:id=类名(首字母小写)。或者通过自定义id来获取实现类的代理对象。