web工程路径¶
配置tomcat运行快捷键
tomcat启动的默认快捷键时shift+f10,可以自定义配置:file-setting-keymap-搜索run,找到右边写有shift+f10的选项,右击选择add keyboard shortcut

直接按下自定义快捷键,会自动识别
如果自定义快捷键已经被映射了,选择leave,不破坏原有的快捷键
- 工程路径问题
我们之前写表单的提交路径都是写的完整路径,比较麻烦,有没有一种方式,让我们提交表单或者超链接的时候,显得更加简单呢?

1.工程路径的解决方案¶
1.1方案一:相对路径¶
说明:页面所有的相对路径,在默认情况下,都会参考当前浏览器地址栏的目录(如:http://ip:port/工程名/)加上请求的资源名来进行跳转。
即页面内所有使用相对路径的静态资源和发出的请求都是以当前页面的URL目录为参考基准的。
以下的工程名是指在tomcat中配置的application context
所以我们可以这样写:

相对路径缺点分析:
有时,我们当前页面要请求的资源不在当前浏览器地址栏的URL目录下,那么要定位到该资源就需要使用类似于../../../ 这样的形式去返回寻找资源。这样做会使文件之间的关系变得复杂且难以理解。
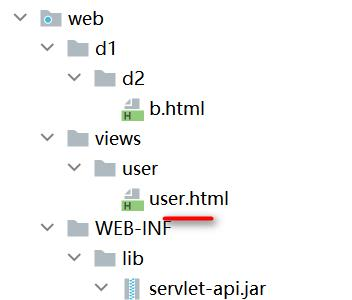
例如:如果我们的tomcat的web文件夹下有如下目录和文件:
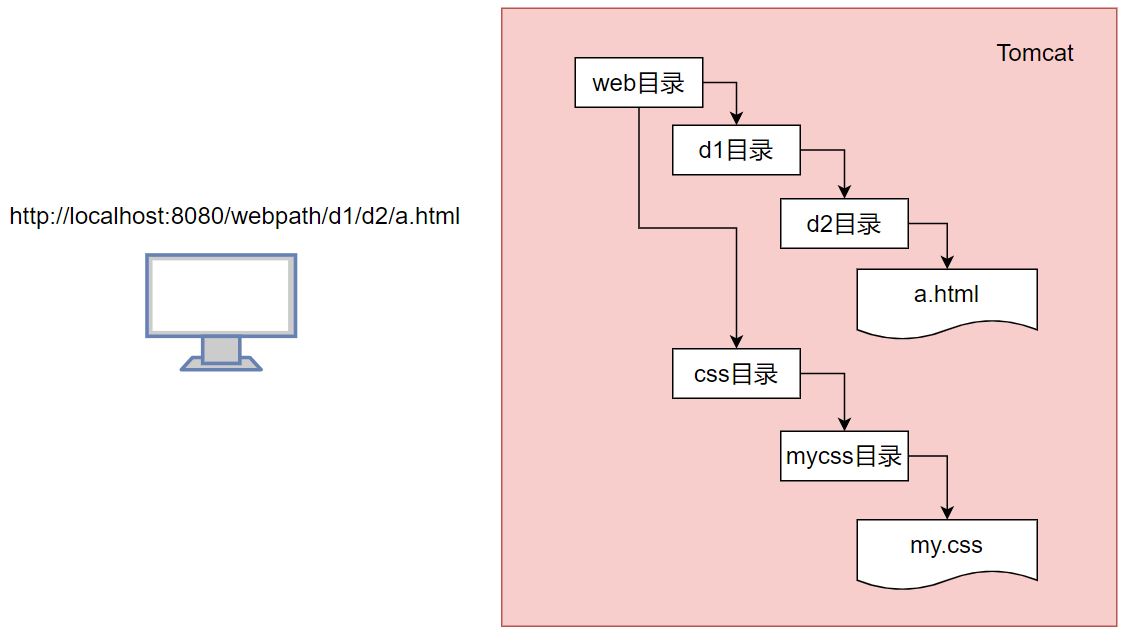
a.html文件要引入my.css的参考路径为../../css/mycss/my.css
使用相对路径时,浏览器会在这个参考路径前面加上当前地址栏的目录来跳转。
这样子就会显得非常繁琐,文件之间的关系变得复杂。我们希望有一种方式可以通过自定义指定URL目录(如ip:port/项目名/xyz/),来定位资源。
解决方案是:使用base标签,指定当前页面所有的相对路径工作时,参照哪个路径来进行跳转
1.2方案二:base标签¶
-
base标签基本介绍
-
base标签是HTML语言中的基准网址标记,它是一个单标签,位于网页头部文件的head标签内
-
一个页面最多只能使用一个base元素,用来提供一个指定的默认目标,是一种表达路径和连接网址的标记
-
常见的URL路径形式分别有绝对路径和相对路径,如果base标签指定了目标,浏览器将通过这个目标来解析当前文档中所有的相对路径,包括的标签有(a,img,link,form)
base标签作用就是自定义参考标准的URL目录,不再跟当前URL有关,对页面内所有使用了相对路径的静态资源路径和请求路径都有效
-
也就是说,浏览器解析时会在路径前加上base给的目录,页面中的相对路径加上目录后就会转换成绝对路径
-
使用了base标签应带上href标签和target标签
-
base应用实例
现在有两个文件,分别是a.html和b.html。a.html文件在web目录下,b.html在web/d1/d2下
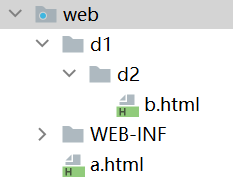
在a.html中引用b.html时,若使用相对路径,参考路径应为:d1/d2/b.html。原因是:当前URL地址栏的目录是http://localhost:8080/webpath/,加上相对路径之后就可以定位到b.html文件
此时由于没有使用base标签,浏览器默认会在参考路径前加上的是当前页面的URL目录
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>a.html</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>这是a.html</h1>
<!--相对路径
1.href="d1/d2/b.html" 这个相对路径 等价于http://localhost:8080/项目名/d1/d2/b.html
-->
<a href="d1/d2/b.html">跳转到/d1/d2/b.html</a>
</body>
</html>
在b.html文件中引用a.html,若只是使用相对路径,参考路径应为:../../a.html。
但是如果我们使用base标签,浏览器在参考路径前加上的就是指定的URL目录
这时若在base中指定URL目录为http://localhost:8080/webpath/,那么参考路径应为a.html。
ps: base标签的写法也可以简化
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>b.html</title>
<!--使用base标签解决
1.base href="http://localhost:8080/webpath/"
表示的含义是当前页面访问的所有资源都是以这个路径为参照的
(即访问的所有资源写的路径前面都会加上这个路径,再去请求资源)
-->
<!--<base href="http://localhost:8080/webpath/">-->
<!--上面的写法可以简化为如下:-->
<base href="/webpath/">
<!--说明如下:
1.base标签是浏览器去解析的
2.浏览器在解析第一个斜杠/的时候,会解析成http://localhost:8080/
3.base href="/webpath/" =解析=> base href="http://localhost:8080/webpath/"
4.而浏览器在解析 <a href="a.html">返回a.html~</a> 时,会参考base,最后是:
href="http://localhost:8080/webpath/a.html
-->
</head>
<body>
<h1>这是/d1/d2/b.html</h1>
<!--
1.要返回a.html 使用相对路径,http://localhost:8080/webpath/d1/d2/
2. ../../a.html => http://localhost:8080/webpath/a.html
3.相对路径会让这个项目相互调用的关系变得复杂
4.使用base标签来解决
-->
<a href="a.html">返回a.html~</a>
</body>
</html>
.gif)
2.服务器转发定位资源¶
在实际开发中,往往不是直接访问一个资源,而是在服务端进行转发或者重定向来访问资源
例子
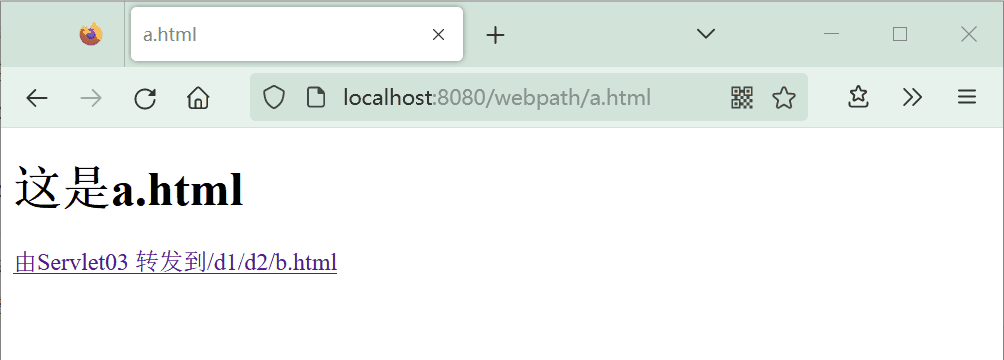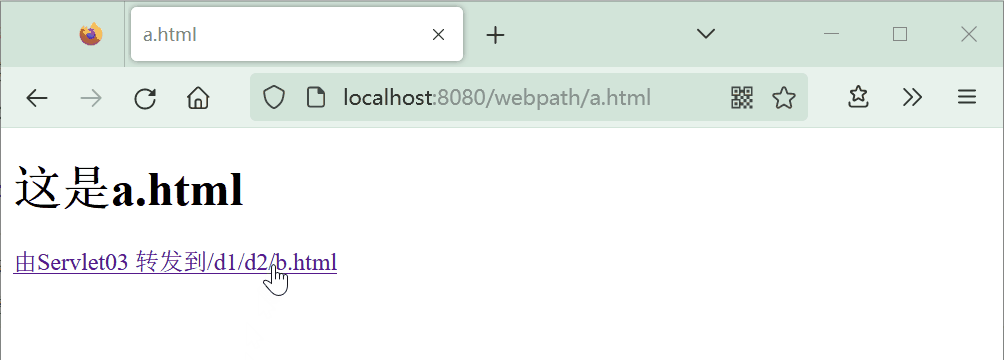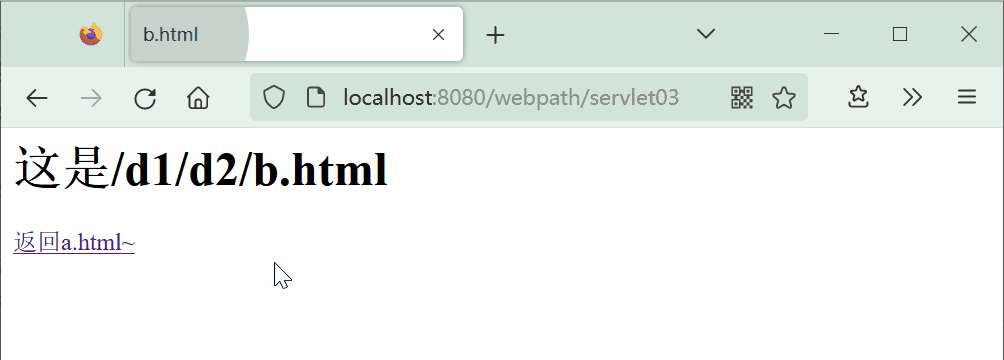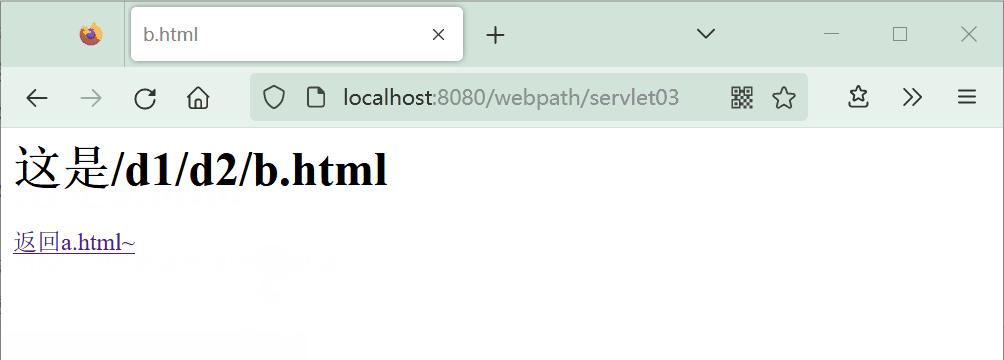
使用上面的a.html和b.html文件。在a.html点击超链接时,浏览器请求servlet03资源,由服务器内部进行转发来访问b.html。
a.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>a.html</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>这是a.html</h1>
<!--演示转发定位b.html
1. href="servlet03"==浏览器解析==>http://localhost:8080/webpath/servlet03
2.
-->
<a href="servlet03">由Servlet03 转发到/d1/d2/b.html</a>
</body>
</html>
servlet03:
请求转发的过程是发生在服务器内部的,因此解析转发的参考路径的是服务器。
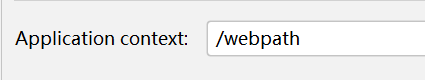
服务器端在解析第一个/时,会被解析成http://ip:port/在tomcat配置的Application context
package com.li.servlet;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Servlet03 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//这里我们希望通过转发来定位到b.html
/**
* 解读:
* 1.服务器端在解析第一个/时,会被解析成http://ip:port/Application context
* 因为转发是发生在服务端的,所以也可以理解为“/”被解析成“/项目名[Application context]”
* 2. /d1/d2/b.html ==解析成=> http://ip:post/项目名/d1/d2/b.html
*/
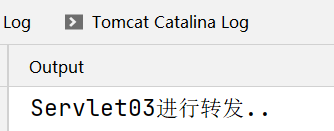
System.out.println("Servlet03进行转发..");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/d1/d2/b.html").forward(request, response);
//相对路径:如果没有带第一个斜杠 d1/d2/b.html,也可以转发成功。
// 因为在服务器进行转发的时候,没有/ 就按照默认的方式参考定位 http://ip:post/项目名/
//但是建议带上/
}
}
b.html不变。
后台输出:
3.练习¶
3.1练习web路径¶
- 创建一个login.html页面,通过以下URL访问
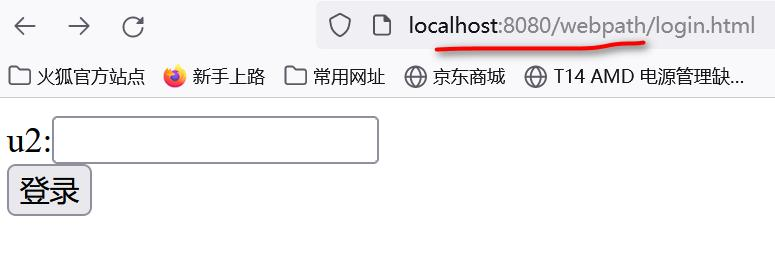
- 创建user.html页面,通过以下URL访问
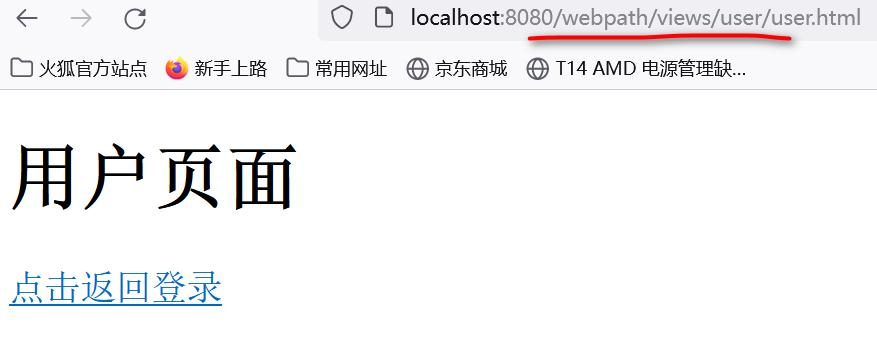
- 请写出login.html在不通过servlet转发情况下,如何通过表单提交,找到user.html,把所有的写法列出来
这里通过服务器渲染技术可以动态得到 /工程路径,在之后会讲
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>login.html</title>
<!-- <base href="/webpath/views/user/">-->
</head>
<body>
<!--从login.html跳转到user.html
1.使用绝对路径 action="http://localhost:8080/webpath/views/user/user.html"
2.使用相对路径 action="views/user/user.html"
3.使用base+相对路径
action="user.html" & <base href="http://localhost:8080/webpath/views/user/">
4.简化base+相对路径 -浏览器在解析base的第一个/时,会解析成 http://ip:port/
action="user.html" & <base href="http://localhost:8080/webpath/views/user/">
5.根据4.可以去掉base,直接写action="/webpath/loginServlet"
浏览器默认将第一个/解析为http://ip:port/
-->
<form action="/webpath/views/user/user.html" method="post">
u2: <input type="text" name="username"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="登录"/><br/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
- 请写出login.html在通过servlet转发的情况下(自定义servlet),如何通过表单提交,找到user.html,把所有的写法列出来
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>login.html</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--这里的action也有几种写法,同上-->
<form action="loginServlet" method="post">
u2: <input type="text" name="username"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="登录"/><br/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
package com.li.servlet;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.annotation.*;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = {"/loginServlet"})
public class loginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//这里是服务器解析:前面默认加上 http://ip:port/Application context
request.getRequestDispatcher("/views/user/user.html").forward(request, response);
//或者相对路径 views/user/user.html,最前面没有/,就按照默认的方式参考定位 http://ip:post/Application context/
}
}
- 请写出 在 user.html,点击返回登录,可以重新回到到 login.html,把所有的写法都列出来
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>user.html</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>用户页面</h1>
<!--回到a.html
1.使用绝对路径 href="http://localhost:8080/webpath/login.html"
2.使用相对路径 href="login.html"
(这里因为login.html是请求转发到的user.html,因此浏览器当前的URL为
http://localhost:8080/webpath/loginServlet
即当前的URL目录为http://localhost:8080/webpath/ )
3.使用base+相对路径
<base href="http://localhost:8080/webpath/"> & <a href="login.html"></a>
4.使用简化base+相对路径-浏览器在解析base的第一个/时,会解析成 http://ip:port/
<base href="/webpath/"> & <a href="login.html"></a>
5.根据4.可以去掉base,直接将超链接写成<a href="/webpath/login.html">
浏览器默认将第一个/解析为http://ip:port/
-->
<a href="/webpath/login.html">点击返回登录</a>
</body>
</html>
4.工程路径注意事项和细节¶
- web工程的相对路径和绝对路径
相对路径是:
.表示当前目录..表示上一级目录资源名表示当前目录/资源名
绝对路径:http://ip:port/工程路径/资源路径
-
在实际的开中,路径都使用绝对路径,而不是相对路径
-
在web中
/斜杠 如果被**浏览器**解析,得到的地址是http://ip[域名]:port/ -
在web中
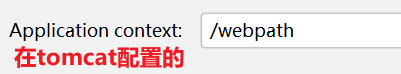
/斜杠 如果被**服务器**解析,得到的地址是http://ip[域名]:port/工程路径,下面的几种情况就是如此: -
<url-pattern>/servleturl</url-pattern> servletContext.getRealPath("/")request.getRequestDispatcher("/")
realPath是项目的工作路径(执行路径),contextPath是我们配置的application context


- 在javaweb中,路径最后带/和不带/,两者含义是不同的,一定要注意
比如:<a href="/a/helloServlet">网址</a> 中的helloServlet表示资源
<a href="/a/helloServlet/">网址</a> 中的helloServlet表示路径
- 在重定向中
response.sendRedirect("/");这条语句虽然是在服务器执行的,但是服务器是将 / 发送给浏览器解析,因此得到的地址是http://ip[域名]:port/
小结:在编写资源路径时,要考虑以下几点:
(1)这个路径前面有没有 /,没有就是相对路径
(2)这个路径在哪里被解析(服务器还是浏览器)
(3)路径最后带/和不带/,两者含义不同,没有就是资源,有就是路径
编写资源路径时,首先分析使用绝对路径还是相对路径:
- 如果路径最开始带了 /,直接分析此斜杠在服务器还是浏览器来解析的(斜杠会被怎样解析),再在后面写对应的值:
浏览器解析,/ 是 http://ip[域名]:port/
服务器解析,/ 是http://ip[域名]:port/工程路径
- 如果路径最开始没有带 /,按照相对路径去分析,分析浏览器当前URL目录还是你写的base标签的值来解析。再在后面写对应的值
不推荐第二种写法,这种方法依赖于浏览器当前URL目录
5.练习2¶
在3.1练习的基础上,请写出login.html在通过servlet重定向的情况下,如果通过提交表单,找到user.html,把所有的写法列出来
login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>login.html</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/webpath/servlet02" method="post">
u2: <input type="text" name="username"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="登录"/><br/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
servlet02:
package com.li.servlet;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.annotation.*;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = {"/servlet02"})
public class Servlet02 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1.response.sendRedirect("views/user/user.html");//相对路径定位
//2.response.sendRedirect("/webpath/views/user/user.html");
//3.(推荐)
String contextPath = getServletContext().getContextPath();
response.sendRedirect(contextPath + "/views/user/user.html");
}
}
user.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>user.html</title>
<base href="/webpath/">
</head>
<body>
<h1>用户页面</h1>
</body>
</html>
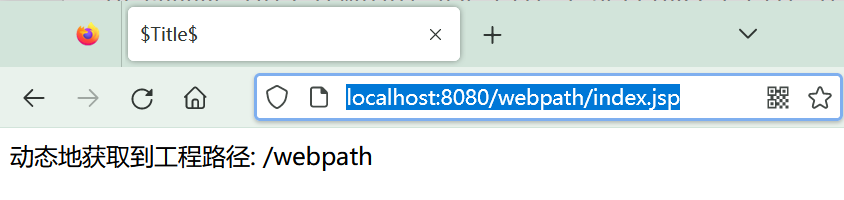
6.优化web工程路径¶
在前面的base案例中,我们可以对路径进行优化
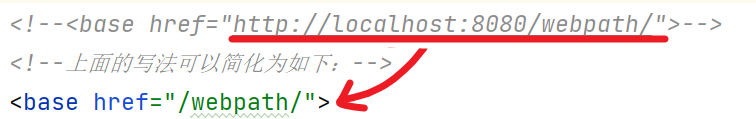
如上图,我们希望在写项目路径时动态获取,而不是直接写死,这样修改了项目路径之后也不会出错。
如果如何动态获取呢?
使用 jsp 或者 thymeleaf 加入标签,动态获取即可
例子-index.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" isELIgnored="false" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>$Title$</title>
</head>
<body>
动态地获取到工程路径: <%=request.getContextPath()%>
</body>
</html>