JDBC和连接池03¶
8.事务¶
8.1事务介绍¶
-
基本介绍
-
JDBC程序中当一个Connection对象创建时,默认情况下是自动提交事务:每次执行一个SQL语句时,如果执行成功,就会向数据库自动提交,而不能回滚。
- JDBC程序中为了让多个SQL语句作为一个整体执行,需要使用事务
- 调用Connection的setAutoCommit(false)可以取消自动提交事务
- 在所有的SQL语句都执行成功后,调用Connection的commit();方法提交事务
- 在其中某个操作失败或者出现异常时,调用Connection的rollback();方法回滚事务


8.2事务处理¶
应用实例
模拟经典的转账业务
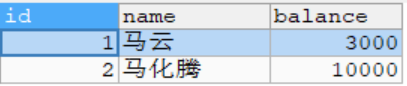
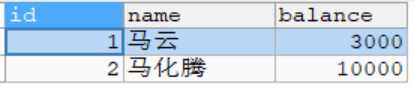
首先创建一张account表,插入两条数据
CREATE TABLE ACCOUNT(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
NAME VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
balance DOUBLE NOT NULL DEFAULT 0
)CHARACTER SET utf8;
INSERT INTO ACCOUNT VALUES(NULL,'马云',3000),(NULL,'马化腾',10000);
SELECT * FROM ACCOUNT;
package li.jdbc.transaction_;
import li.jdbc.utils.JDBCUtils;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* 演示JDBC中如何使用事务
*/
public class Transaction_ {
//没有使用事务
@Test
public void noTransaction() {
//操作转账业务
//1.得到连接
Connection connection = null;
//2.组织sql语句
String sql = "update account set balance=baLance-100 where id=1";
String sql2 = "update account set balance=baLance+100 where id=2";
//3.创建PreparedStatement对象
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();//在默认情况下,connection默认自动提交
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); //执行第一条sql
int i = 1 / 0;//抛出异常--模拟异常可能--可以看到出现异常状态之后的语句没有执行
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql2);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();//执行第二条sql
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭资源
JDBCUtils.close(null, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
//使用事务来解决
@Test
public void useTransaction() {
//操作转账业务
//1.得到连接
Connection connection = null;
//2.组织sql语句
String sql = "update account set balance=baLance-100 where id=1";
String sql2 = "update account set balance=baLance+100 where id=2";
//3.创建PreparedStatement对象
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();//在默认情况下,connection默认自动提交
//将connection设置为不自动提交
connection.setAutoCommit(false);//开启了事务
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); //执行第一条sql
int i = 1 / 0;//抛出异常
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql2);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();//执行第二条sql
//在这里提交事务
connection.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
//如果在try里面出现了异常,就会进入catch语句,
// 这意味着我们可以在catch语句里面进行回滚,即撤销执行的SQL语句
System.out.println("执行发生了异常,撤销已执行的SQL");
try {
connection.rollback();//没有填写保存点就默认回滚到事务开始的状态
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭资源
JDBCUtils.close(null, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
}
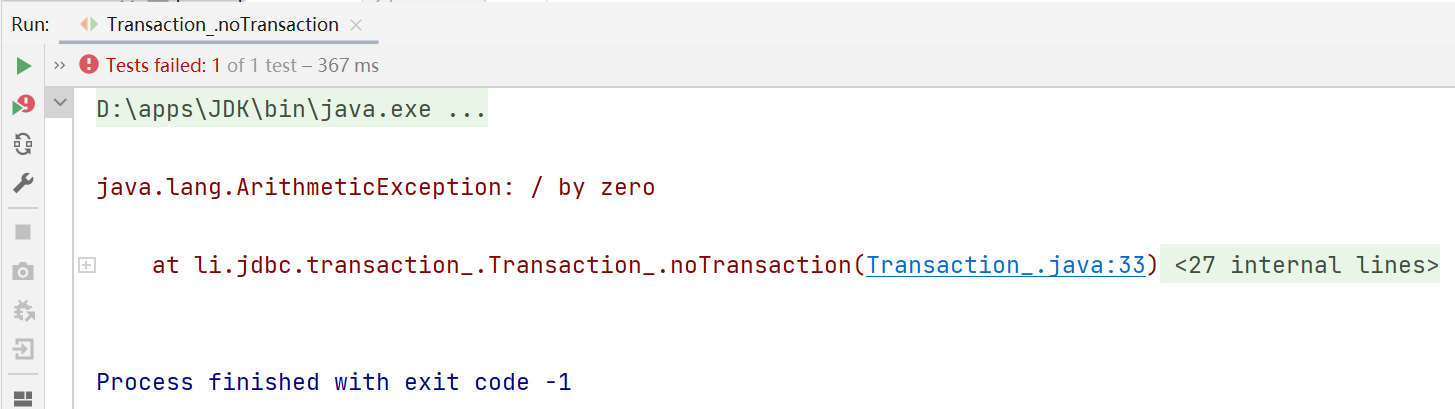
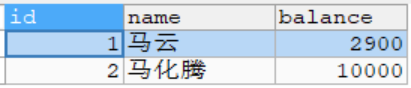
- 没有使用事务(noTransaction)的运行结果:可以看到因为默认为直接提交事务,在出现异常后没有执行异常后面的语句就进入了catch语句,造成数据错误
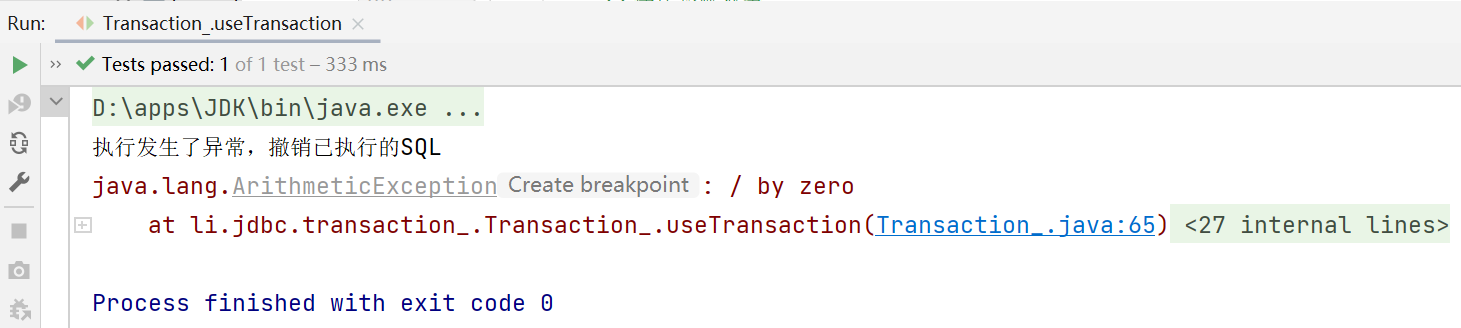
- 使用了事务(useTransaction)之后:可以看到由于在catch语句中进行了回滚操作,在捕获到异常之后直接进行回滚,保证数据的一致性
9.批处理¶
-
基本介绍
-
当需要成批插入或者更新记录时,可以采用Java的批量更新机制,这一机制允许多条语句一次性提交给数据库批量处理。通常情况下比单独提交处理更有效率
- JDBC的批量处理语句包括下面方法:
- addBatch():添加需要批量处理的SQL语句或参数
- executeBatch():执行批量处理语句
- clearBatch():清空批处理包的语句
- JDBC连接MySQL时,如果要使用批处理功能,请在url中加参数**?rewriteBatchedStatements=true**
- 批处理往往和PreparedStatement一起搭配使用,可以既减少编译次数,又减少运行次数,效率大大提高
9.1批处理应用¶
例子
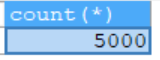
- 演示向admin2表中添加5000条数据,看看使用批处理耗时多久
- 注意批处理需要修改配置文件的数据:url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/数据库?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
user=root
password=123456
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hsp_db02?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
首先创建测试表admin2
CREATE TABLE admin2(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
username VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL,
PASSWORD VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL );
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM admin2;
测试程序:
package li.jdbc.batch_;
import li.jdbc.utils.JDBCUtils;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* 演示java的批处理
*/
public class Batch_ {
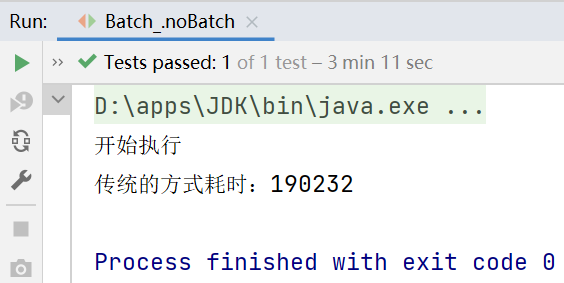
//传统方法,添加5000条数据到admin2
@Test
public void noBatch() throws Exception {
//获取连接
Connection connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//sql
String sql = "insert into admin2 values (null,?,?)";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
System.out.println("开始执行");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
preparedStatement.setString(1, "jack" + i);
preparedStatement.setString(2, "666");
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("传统的方式耗时:" + (end - start));
//关闭连接
JDBCUtils.close(null, preparedStatement, connection);
}
//使用批量方式添加数据--注意在配置文件添加参数?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
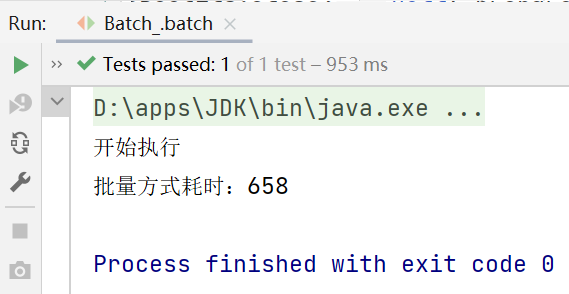
@Test
public void batch() throws Exception {
//获取连接
Connection connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//sql
String sql = "insert into admin2 values (null,?,?)";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
System.out.println("开始执行");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
preparedStatement.setString(1, "jack" + i);
preparedStatement.setString(2, "666");
//将SQL语句加入到批处理包中
preparedStatement.addBatch();
//当有1000条SQL时,再批量执行
if ((i + 1) % 1000 == 0) {//每满1000条时,就批量执行
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
//执行完就清空批处理包
preparedStatement.clearBatch();
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("批量方式耗时:" + (end - start));
//关闭连接
JDBCUtils.close(null, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
9.2批处理源码分析¶
在上述代码中,在preparedStatement.addBatch();语句旁打上断点,点击debug,点击step into

可以看到光标跳转到了如下方法:
public void addBatch() throws SQLException {
if (this.batchedArgs == null) {
this.batchedArgs = new ArrayList();
}
this.batchedArgs.add(new PreparedStatement.BatchParams(this.parameterValues, this.parameterStreams, this.isStream, this.streamLengths, this.isNull));
}
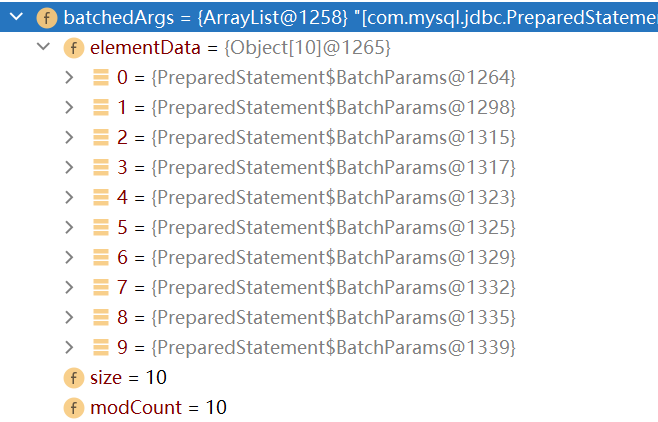
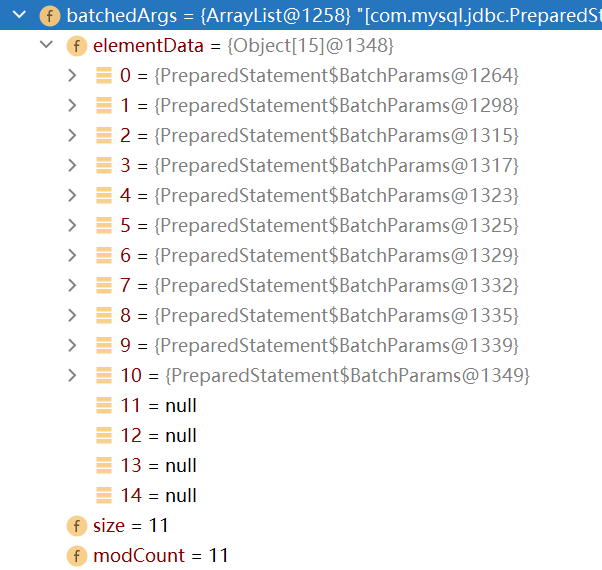
第一次执行该方法时,会创建Arraylist类型的对象集合elementDate=>Object[],elementDate=>Object[]用来存放我们预处理的SQL语句。当elementDate满后,就按照1.5倍扩容
当添加到指定的值后,就会执行executeBatch();
批处理会减少我们发送SQL语句的网络开销,并且减少编译次数,因此效率提高了
1.5倍扩容:
9.3.事务和批处理的区别¶
-
事务: 事务底层是在数据库方存储SQL,没有提交事务的数据放在数据库的临时表空间。 最后一次提交是把临时表空间的数据提交到数据库服务器执行 事务消耗的是数据库服务器内存
-
批处理:
批处理底层是在客户端存储SQL 最后一次执行批处理是把客户端存储的数据发送到数据库服务器执行。 批处理消耗的是客户端的内存